A line of credit is a loan that gives you flexible access to capital on an as-needed basis. It’s a versatile financial tool that can be either secured or unsecured. So what’s the difference between unsecured vs. secured line of credit options? Simply put, a secured line of credit is backed by collateral, while an unsecured line of credit is not.
Secured and unsecured lines of credit are two contrasting approaches to borrowing, each with its own advantages, requirements, and potential risks. We’ll lay out the differences, guide you through the process of choosing between the two, and cover alternatives, all to empower you to make the best choice for your business financing needs.
Key takeaways
- Secured lines of credit are backed by collateral.
- Unsecured lines of credit are not backed by collateral.
- Secured lines of credit have lower interest rates and larger borrowing limits, while unsecured lines of credit have quick setups and more usage flexibility.
What is a secured line of credit?
A secured line of credit is a flexible borrowing arrangement where a business can access funds up to a certain limit, backed by collateral in case the loan isn’t repaid. For businesses, a secured line of credit relies on collateral such as real estate, equipment, inventory, receivables, or other valuable assets to back up the loan. If the borrower defaults, the lender can claim the collateral to recover their loss.
Lenders prefer secured lines of credit because they carry reduced risk. This results in lower interest rates and larger borrowing limits for the borrower.
An example of secured credit is a construction company using its equipment as collateral to secure a line of credit If the construction company defaults, the lender can then claim the equipment to sell and recover the outstanding debt.
| Secured line of credit pros | Secured line of credit cons |
| • Lower interest rates since the lender’s risk is reduced • Higher credit limits and access to more funds • Easier to be approved, even with a less-than-stellar credit score | • Risk of asset loss if you’re unable to repay the debt • Some have restrictions on how you can use the funds • Setup can be complex with additional paperwork |
What is an unsecured line of credit?
An unsecured line of credit, on the other hand, does not require any collateral. The lender offers the loan based purely on the borrower’s creditworthiness, financial performance, and cash flow.
While this eliminates the risk of losing an asset, unsecured lines of credit typically have a more stringent eligibility process and higher interest rates to compensate for the lender’s increased risk.
Banks rarely offer unsecured financing, but private credit lenders do. Private credit enables borrowers to access capital without collateral coverage while providing a faster, relationship-focused process.
An example of an unsecured line of credit is a restaurant that’s approved based on strong credit history and cash flow. The restaurant uses the funds to hire additional staff for large special events. There is no collateral involved.
| Unsecured line of credit pros | Unsecured line of credit cons |
| • No collateral required, so you don’t risk losing an asset if you can’t repay • Flexibility in how you use the funds • Quick setup, as there’s no need to establish collateral ownership | • Higher interest rates due to higher risk for lenders • Lower credit limits/access to less capital • Strong credit is required since approval is harder without collateral |
What is the difference between secured and unsecured credit?
As you can see, secured and unsecured business lines of credit differ in collateral requirements, interest rates, credit limits, approval difficulty, and more. Let’s lay out these differences side by side:
| Basis of comparison | Secured line of credit | Unsecured line of credit |
| Collateral requirement | Collateral is required as security against the credit line. | No collateral is needed. |
| Interest rates | Rates are usually lower. | Rates are usually higher. |
| Credit limit | Higher borrowing limits are easier to negotiate. | Lower borrowing limits |
| Approval difficulty | It’s easier to get approved if you have an asset of significant value to use as collateral. | It can be harder to get approved, especially for those with weaker credit. |
| Use of funds | You may be limited to a specific purpose (e.g., a line of credit secured by equipment, or you may need to use inventory for operational expenses or asset purchases). | There are generally no restrictions on the use of funds. |
| Risk to borrower | If the borrower defaults, they risk losing the asset used as collateral. | Defaulting can lead to lawsuits, wage garnishments, and credit score damage. |
Now that you know the key differences, let’s discuss how to choose the right option for your business.
How to choose between a secured vs. unsecured line of credit
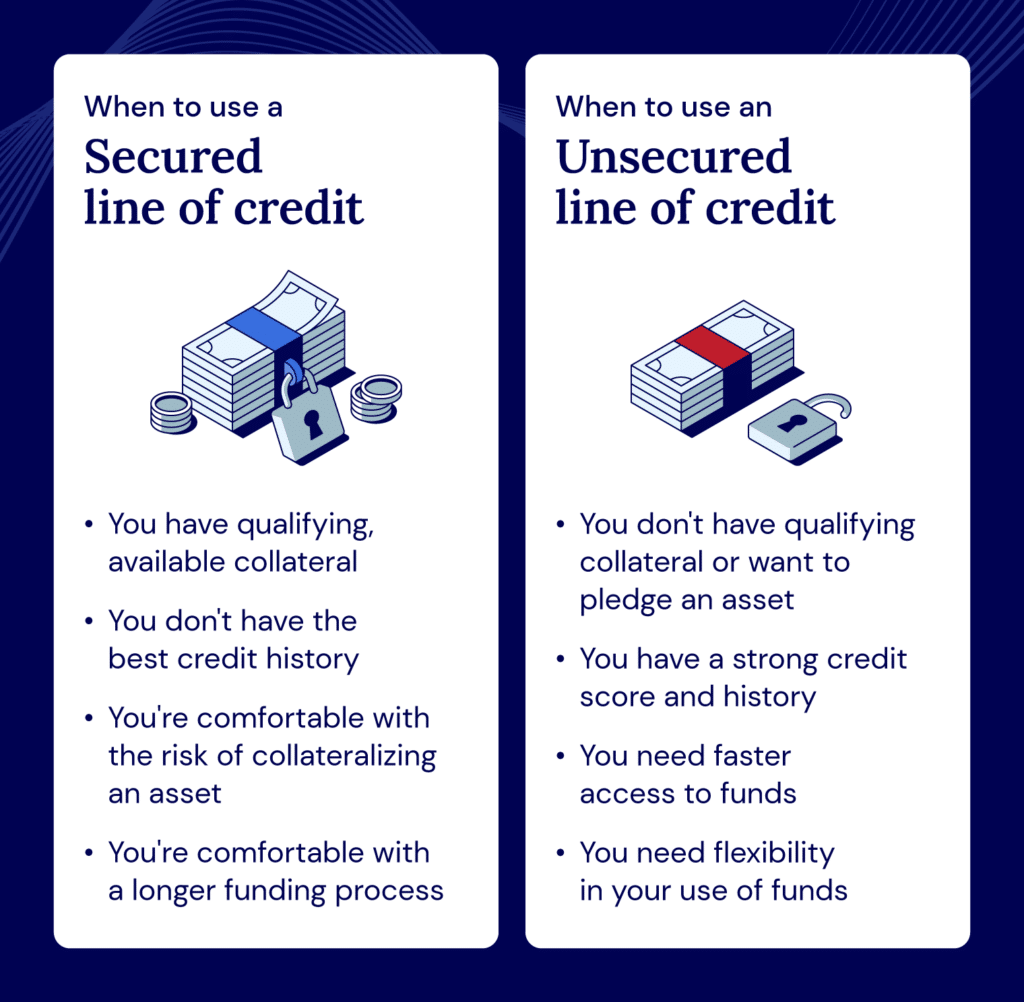
So, which line of credit type is right for your business? To decide, you’ll need to consider your ability to provide collateral, your credit score, the amount of capital you need to borrow, the interest rates on offer, and your timeline needs.
Consider collateral availability and risk tolerance
A secured line of credit may be a better option for businesses that have assets to pledge and are willing to risk those assets. Unsecured lines of credit may be best if you don’t have these assets or want to risk losing one.
Note credit profile and qualification requirements
Lenders may be more flexible on credit score for a secured line of credit since they are backed by collateral. Because unsecured lines of credit are riskier than secured ones, lenders are choosier about who they lend to. Therefore, you often need a strong credit history to qualify for an unsecured line of credit.
Here’s an overview of how qualification requirements may differ:
| Secured line of credit | Unsecured line of credit |
| Assessment of assets: Lenders will assess the value of your assets that can be used as collateral. | Credit score check: Lenders will thoroughly check your credit score, which often needs to be good or excellent. |
| Credit history review: Lenders will review your credit history, although they might be more flexible on credit score since they’re backed by collateral. | Income verification: To prove that you can repay the loan, you must provide proof of income (ex., pay stubs, tax returns, or bank statements). |
| Financial review: The lender will review your financial statements (including a review of income, existing debts, and overall financial health) to assess your ability to repay the loan. | Review of financial health: Lenders will review your existing debts, financial standing, and sometimes a business plan. |
| Approval and terms: If approved, the lender will establish terms for the line of credit, including the credit limit, interest rate, and repayment schedule. | Approval and terms: If approved, the lender will provide you with the terms of the credit line, including the credit limit, interest rate, and repayment schedule. |
Keep in mind that the qualification process for both secured and unsecured lines of credit largely depends on the lender’s requirements.
Assess your funding amount and timeline needs
An unsecured line of credit may be better for businesses that need quick access to funding but not as large a credit limit, and are willing to pay higher interest fees.
On the other hand, a secured line of credit may be best if you need to borrow more. It also usually has longer repayment terms.
To summarize, a secured line of credit might be more suitable if you can provide collateral and require a larger loan with lower interest rates. If you have a strong credit score, need funds quickly, and don’t want to risk an asset, an unsecured line of credit may be more appropriate.
Alternatives to business lines of credit
As a business owner, it’s important to consider all your financing options. Here are some alternatives to business lines of credit to consider:
- Cash flow financing: Cash flow financing is a type of short-term financing that involves a loan backed by your business’s expected cash flow.
- Term loans: With a term loan, you borrow a lump sum upfront with an agreed repayment schedule and specific borrowing terms.
- Invoice factoring: Invoice factoring is a type of accounts receivable financing in which you sell your outstanding invoices to a third party. This allows your business to raise capital up front.
- Equipment financing: Equipment financing lets businesses purchase equipment without paying the full cost upfront. You can use it to buy equipment like machinery, vehicles, and office furniture.
- SBA funding: An SBA loan is guaranteed by the Small Business Administration. You can use this type of loan for various goals, like buying equipment and expanding.
Doing in-depth research on all your options will help you make the most educated choice when it comes to your specific financial situation and business needs.
Find the flexible funding you need with National Business Capital
Weighing secured vs. unsecured lines of credit depends heavily on your individual business. While secured lines of credit often have lower interest rates and higher borrowing limits, they do carry the risk of losing the collateral you’ve pledged in case of default. On the other hand, unsecured lines of credit may be faster to obtain and don’t require collateral, but typically come with higher interest rates and more stringent credit requirements.
If choosing the right financing option still feels overwhelming, we at National Business Capital can help. Our expert business advisors are here to answer your questions and guide you through everything you need to find the best financing options for your business.
Whether you need inventory financing or another financing option, we’re here to propel your business forward. We offer various lines of credit options to help your company take that next important step. Fill out your online application to get started.
Frequently asked questions
The draw period is when a business can access funds from its line of credit. Once it’s over, the company has to start repaying the outstanding balance and can no longer draw additional funds.
The repayment terms tell you exactly when and how you need to repay the borrowed funds. They may dictate the repayment period, the minimum payment required, and more.
There are risks associated with both secured and unsecured lines of credit if you default.
With a secured line of credit, the primary risk is that you could lose the asset you’ve pledged as collateral if you’re unable to repay the borrowed amount. This could be a property, equipment, or other valuable assets.
For an unsecured line of credit, the risk lies in the potential for damage to your credit score if you fail to make repayments. This can make it more challenging to secure credit in the future. Additionally, lenders may take legal action if you fail to repay.
Real estate, equipment, business inventory, or other high-value assets are commonly used as collateral for a secured line of credit. The type of assets accepted as collateral may vary depending on the lender’s policies.
If you default on a secured line of credit, the lender has the right to seize the asset you’ve used as collateral to recover the debt. In the case of an unsecured line of credit, the lender may report the default to credit bureaus, negatively affecting your credit score. They may also sue you to recover their funds.


